While the occasional inflamed throat—that usually passes without major drug intervention—signals that your body’s immune system is in shape, chronic inflammation is associated with various diseases, such as arthritis, allergies, Parkinson’s, cancer, autism, and even mental illness. Luckily, studies show that changing your diet is one of the key options for keeping inflammation at bay. The list of foods that fight inflammation effectively is fortunately long and tasty. [1]
Here we discuss four such foods, plus one other natural remedy to fight inflammation—CBD oil.
In the words of researcher Dr. Paul DiCorleto, PhD: [3]

How can your diet help your body fight inflammation? Let’s take a look at the science behind the four groups of foods that most effectively fight inflammation.
1. Fish
Rich in omega fatty acids, various types of fish show potential anti-inflammatory effects. Several studies examined the relationship between omega fatty acids and inflammatory processes.
A 2010 article, published in the online open-access journal Nutrients, concluded that certain long-chain fatty acids influence inflammation through a variety of mechanisms. Especially Omega-3 fatty acid shows therapeutic efficacy in a long list of inflammatory conditions. [2]

Although further research is needed, one example of how inflammation affects the body is with its role in heart attack or stroke. It is assumed that if inflammatory-fighting cells stay in the system for too long, they promote the buildup of dangerous plaque in the circulatory system. Since the body doesn’t recognize the plaque, it sends more of its anti-inflammatory responders to fight it. If the buildup continues, the arteries are likely to become thicker, increasing the risk of heart attack or stroke. [3]
Ensure a weekly fish intake of salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines. A recommended dose by the American Heart Association is three to four ounces of fish, twice a week. [4]
Alternatively, you can take a good fish-oil supplement.
RELATED: How CBD May Help With Inflammation and Allergies
2. Olive Oil
The foods in discussion are part of the well-known Mediterranean diet, which is commonly recommended for its anti-inflammatory properties.
According to a study, a traditional Mediterranean diet has good anti-inflammatory effects because of the high intake of virgin olive oil, recommended as part of this dietary regime. Its anti-inflammatory functions are believed to be due to an antioxidant compound found in olive oil, called oleocanthal. [5]
Other studies confirm and support this. One study showed that oleocanthal acted “as a natural anti-inflammatory compound that has the potency and profile strikingly similar to that of ibuprofen.” Ibuprofen is a commonly-prescribed anti-inflammation medication with serious side-effects. [6]
However, it seems that the strongest effects of olive oil surface when combined with fish oil. The combination of the omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil and the antioxidants in olive oil helped users with rheumatoid arthritis to improve joint pain and morning stiffness more than those who took only omega-3. [7]
An article by the Arthritis Foundation also recommended the Mediterranean diet for battling chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, and osteoporosis. [4]

RELATED: Could CBD Be Inflammation’s Worst Enemy ... Naturally?
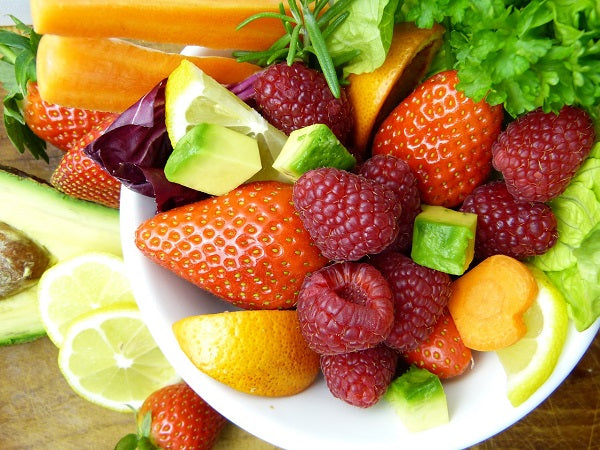
3. Fruits and Vegetables
From strawberries, oranges, and cherries to greens like spinach, kale, broccoli and cabbage, many fruits and vegetables are known to fight inflammation. Leafy greens get their anti-inflammatory power from vitamin K, while the fruits have a type of pigment that helps fight inflammation. [12]
Fruits and vegetables are furthermore rich in antioxidants. Antioxidants are potent chemicals that protect cells.
Other anti-inflammatory fruits are citrus fruits, such as oranges, grapefruits, and limes, because they are loaded with vitamin C. Vitamin C also shows anti-inflammatory properties that can help promote joint health. [4]

4. Nuts
In a 2011 study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition Research, men and women compared the health benefits of nuts in people who consumed the most nuts and those who ate the fewest. This longitudinal study was conducted over 15 years. The results showed that the group that ate the most nuts had a 51 percent “lower risk of dying from an inflammatory disease,” compared to the other group.
5. CBD Oil—A Miracle Anti-inflammation Supplement
Cannabidiol (CBD) in the form of oil, administered sublingually, has been proven an effective anti-inflammatory remedy. A 2009 review discusses a study that showed that daily oral administration of 5 mg/kg CBD inhibited progression of rheumatoid arthritis in mice. The review also explains studies demonstrating CBD's therapeutic action in atherosclerosis, diabetes and diabetic retinopathy. [8]
Although further research is needed, a study performed on rats with intervertebral disc degeneration showed that CBD, in larger doses such as 120 nmol compared to 30 and 60 nmol, significantly attenuated the effects of the disc injury the mice suffered. This indicated that CBD could be helpful in people with intervertebral disc degeneration, which is also associated with chronic inflammation. [9]
When does inflammation become a problem and how can CBD oil help?
As mentioned, inflammation is part of the body’s natural response to infection and tissue damage. It is, in fact, crucial to the body’s healing processes.
Minor infections, allergies, or injuries activate your body’s natural response. To defend itself, the body starts sending cytokines—chemicals also known as “emergency signals”—to activate the immune cells, hormones, and hormone-like substances. All these compounds work together to heal the damaged area. During the healing process, you might be in pain or have a fever, but your body should experience a gradual decrease in inflammation. [10]
However, if inflammation persists for too long, or simply reoccurs in places where your body doesn't need it, it can set off disease processes. Chronic inflammation causes your body to be on a continuous high alert, and this prolonged state of emergency can damage your heart, brain, and other organs. [3]
Because of its anti-inflammatory effects, CBD is considered a novel remedy. It can modulate the function and secretion of cytokines from the immune cells in the body. According to research, “cannabinoids (CBD and THC) suppress the inflammatory response (by suppressing cytokines) and subsequently attenuate disease symptoms”.
CBD and THC may be beneficial in cancers triggered by chronic inflammation, according to research, and can possibly inhibit tumor growth by attenuating inflammation. [11] [8]
RELATED: CBD Edibles Vs. Marijuana Edibles: All You Need to Know
Avoid Food that May Cause Inflammation
All of these foods, as well as CBD, act as natural remedies to prevent or soothe inflammation, but there is another side to the coin—foods that cause inflammation. According to Harvard Health, the following foods should be avoided or limited as much as possible: [13]

These foods are all pro-inflammatory. Margarine, in particular, contains trans fats, which raises LDL cholesterol that also causes inflammation. [12]
Even though we tend to “cheat” and indulge in foods that are not healthy, it is important to include other foods that fight inflammation in our everyday diet. Creating a balance by using the 80/20 rule (80 percent healthy food, 20 percent "cheats"), and making healthy choices in general, increase our chances for a pain-free life. Try to incorporate as many of these foods as you can, even if sometimes that means a daily intake of olive oil, CBD oil, or fish oil, preferably with a large bowl of fresh salad.
Sources:
- https://www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/vanderbiltmedicine/the-good-the-bad-and-the-ugly-of-inflammation/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257651/
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/why-you-should-pay-attention-to-chronic-inflammation/
- https://www.arthritis.org/living-with-arthritis/arthritis-diet/anti-inflammatory/the-arthritis-diet.php
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21443487
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16136122
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15723739
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828614/ [Under: Cannabinoids & RA; Cannabinoids & other inflammatory diseases] [Under: Future perspective]
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4269422/
- https://www.johnshopkinshealthreview.com/issues/spring-summer-2016/articles/understanding-inflammation
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16023222/
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/anti-inflammatory-diet-road-to-good-health#1
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/foods-that-fight-inflammation